Understanding the Importance of Architecture Modeling

The world of architecture is not solely about creating structures; it is about transforming concepts into tangible representations. This is where the art of architecture modeling comes into play. By creating scaled physical or digital representations of buildings, architects are able to visualize their designs, explore various options, and communicate their ideas effectively with clients, stakeholders, and the public. This article delves into the multifaceted significance of architecture modeling, its methodologies, and its role in modern architectural practices.
The Evolution of Architecture Modeling
Architecture modeling has historically evolved alongside advancements in technology and design philosophy. From ancient mudbrick models to cutting-edge 3D digital renderings, the essence of architecture modeling has always remained the same: to provide a clearer understanding of a project before it is brought to life.
1. Historical Context
In ancient civilizations, architects used simple models constructed from materials such as clay, wood, and stone to demonstrate their visions. These early models were crucial for both the creative process and for persuading patrons of the feasibility and aesthetic quality of proposed structures. Fast forward to the Renaissance, and we see the use of intricate models, often built to showcase the grandeur of cathedral designs.
2. The Role of Technology
The introduction of 3D computer-aided design (CAD) software revolutionized architecture modeling. It allowed architects to create detailed and precise models, including virtual walkthroughs of their designs. Additionally, the rise of Building Information Modeling (BIM) has further enhanced the architects' ability to manage not just the design but also the construction process, integrating various project aspects into a cohesive model.
Why Architecture Modeling is Essential for Architects
Architects depend on architecture modeling for various reasons. Here are several key benefits:
- Improved Visualization: Models allow architects and clients to visualize the final product much better than traditional blueprints or sketches.
- Enhanced Communication: Physical models and digital renderings facilitate discussions with clients and team members, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Error Detection: By modeling a design, architects can identify potential issues early in the process, minimizing costly revisions later on.
- Client Engagement: Interactive models can engage clients more effectively, making it easier for them to understand design choices and suggest modifications.
Types of Architecture Modeling
Architecture modeling comes in various forms, each offering its unique advantages. Let's explore the primary types of architecture models used by architects today:
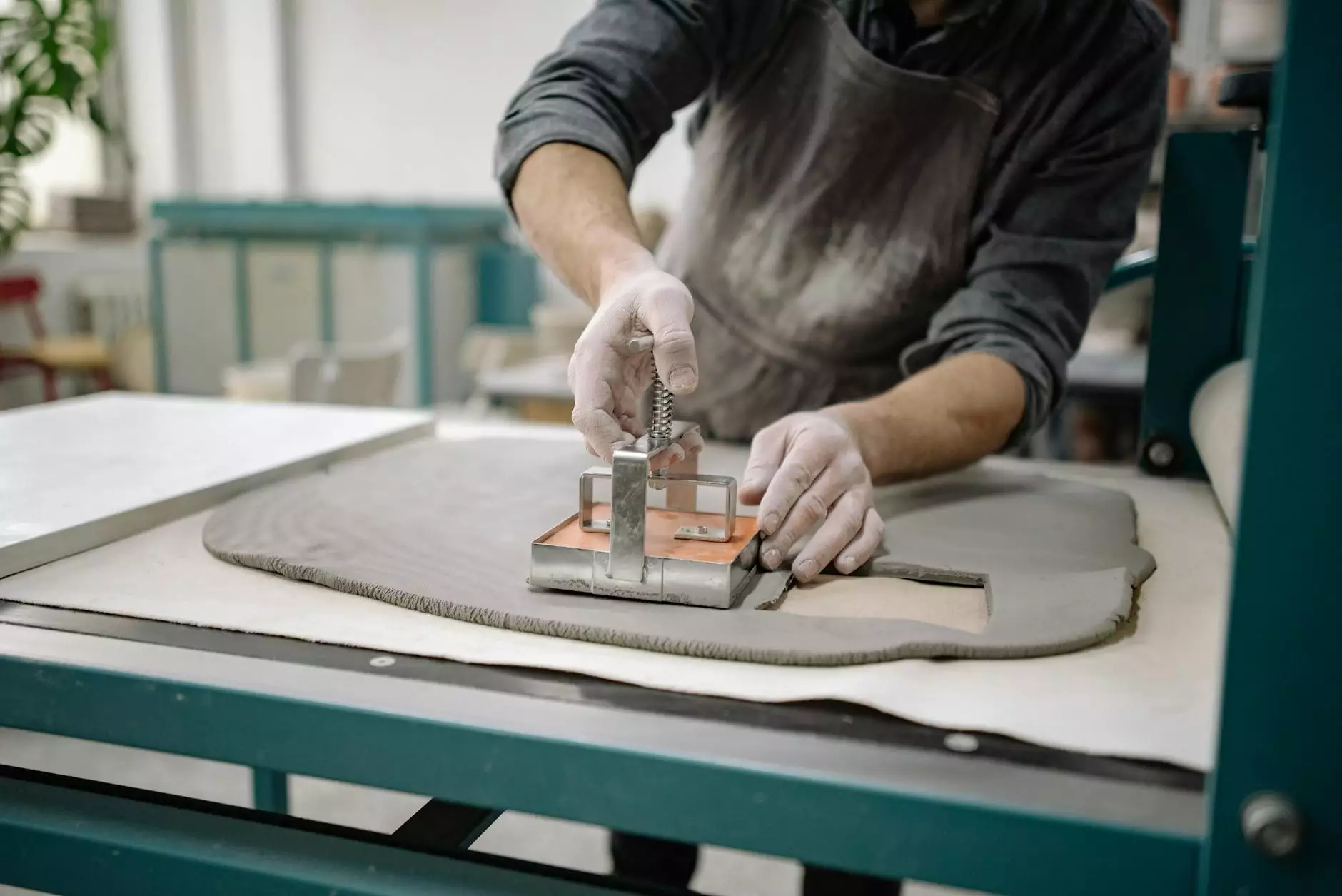
1. Physical Models
Physical architecture models are tangible representations of designs. They can be made out of materials like cardboard, wood, and plastic. Physical models are often used for:
- Presentation: Physical models offer a hands-on way to present a design, allowing viewers to examine it from different angles.
- Scale Representation: The physical scale allows for a better understanding of proportions and spatial relationships.
Creating physical models require craftsmanship and attention to detail, making them an art form in their own right.
2. Digital Models
Digital architecture models utilize advanced software to create highly detailed virtual representations. These models are significant for:
- Visualization: Architects can render photorealistic images and animations to showcase their designs.
- Data Integration: Digital modeling allows for the integration of various project data, improving workflow with BIM.
- Collaboration: Teams can access and manipulate models remotely, facilitating collaboration across different locations.
3. 3D Printed Models
In recent years, 3D printing technology has become an innovative tool in architecture modeling. 3D printed models provide:
- Rapid Prototyping: Architects can quickly produce physical models based on digital designs.
- Precision: 3D printers create highly detailed and accurate models, enhancing representation quality.
The Challenges of Architecture Modeling
While architecture modeling is incredibly beneficial, it also presents certain challenges. Here are some common hurdles architects face:
1. Time and Resources
Developing detailed models, whether physical or digital, can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Architects must balance the need for high-quality modeling with project deadlines and budgets.
2. Keeping Up with Technology
The rapid advancement of modeling technology requires architects to continually update their skills and software. This ongoing education can be demanding but is necessary to stay competitive in the field.
3. Misinterpretation of Models
Even the best models can be misinterpreted by clients or stakeholders. Clear communication and thorough explanations are crucial to prevent misunderstanding.
Best Practices for Effective Architecture Modeling
To maximize the effectiveness of architecture modeling, architects should adhere to several best practices:
- Choose the Right Type of Model: Select the model type that best serves your project’s needs, considering both the complexity of the design and the audience.
- Use Technology Wisely: Invest in up-to-date software and tools that enhance the efficiency and quality of modeling efforts.
- Engage Clients Throughout the Process: Include clients in the modeling phase, allowing for feedback and adjustments.
- Prioritize Clarity: Ensure that models are accompanied by clear explanations and visual aids to facilitate understanding and communication.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Architecture Modeling
Examining specific case studies can illustrate the practical impact of architecture modeling. Here are a couple of notable examples:
1. The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao
Designed by Frank Gehry, the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao is a hallmark of modern architecture that cleverly utilized both physical and digital models during its design phase. Gehry's innovative use of 3D modeling allowed him to explore unconventional forms and structures that resulted in its iconic, organic design.
2. One World Trade Center
The design process of One World Trade Center employed BIM technology extensively. By creating a comprehensive digital model, the architects were able to streamline communication among various teams, enhance collaboration, and address engineering challenges effectively.
The Future of Architecture Modeling
As we look to the future, architecture modeling is poised for even greater advancements. The integration of virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies is rapidly changing the landscape. These immersive tools will allow architects and clients to interact with models in real time, exploring designs as if they were physically present within them. Developers are also focusing on sustainability, using modeling to test energy efficiency and environmental impact, thereby promoting greener architecture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, architecture modeling is a vital element of the architectural process, enabling architects to conceptualize, communicate, and realize their designs. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities and applications of architecture modeling. Embracing these changes will ensure architects remain at the forefront of innovation, ultimately leading to more successful projects that resonate with clients and communities alike. For further exploration and insights into architecture modeling, visit architectural-model.com, your premier resource in understanding the intricacies of architectural design and modeling.